Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Nucleic Acid
Product name
HWTS-OT062-Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (Fluorescence PCR)
Certificate
CE
Epidemiology
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the important pathogenic bacteria of nosocomial infection. Staphylococcus aureus (SA) belongs to the staphylococcus and is a representative of Gram-positive bacteria, which can produce a variety of toxins and invasive enzymes. The bacteria have the characteristics of wide distribution, strong pathogenicity and high resistance rate. Thermostable nuclease gene (nuc) is a highly conserved gene of staphylococcus aureus. In recent years, due to the extensive use of hormones and immune preparations and the abuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, nosocomial infections caused by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Staphylococcus have been on the rise. The national average detection rate of MRSA was 30.2% in 2019 in China. MRSA is divided into healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA), community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA), and livestock-associated MRSA (LA-MRSA). CA-MRSA, HA-MRSA, LA-MRSA have great differences in microbiology, bacterial resistance (eg, HA-MRSA shows more multidrug resistance than CA-MRSA) and clinical characteristics (eg infection site). According to these characteristics, CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA can be distinguished. However, the differences between CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA are narrowing due to the constant movement of people between hospitals and communities. MRSA is multi-drug resistant, not only resistant to β-lactam antibiotics, but also to aminoglycosides, macrolides, tetracyclines and quinolones to varying degrees. There are large regional differences in drug resistance rates and different trends.
Methicillin resistance mecA gene plays a decisive role in staphylococcal resistance. The gene is carried on a unique mobile genetic element (SCCmec), which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) and it has low affinity to β-lactam antibiotics, so that antimicrobial drugs can not hinder the synthesis of cell wall peptidoglycan layer, resulting in drug resistance.
Channel
| FAM | methicillin-resistant mecA gene |
| CY5 | staphylococcus aureus nuc gene |
| VIC/HEX | Internal Control |
Technical Parameters
| Storage | Liquid: ≤-18℃ |
| Shelf-life | 12 months |
| Specimen Type | sputum, skin and soft tissue infection samples, and whole blood samples |
| Ct | ≤36 |
| CV | ≤5.0% |
| LoD | 1000 CFU/mL |
| Specificity | There is no cross-reactivity with other other respiratory pathogens such as methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococcus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, pseudomonas aeruginosa, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumoniae, acinetobacter baumannii, proteus mirabilis, enterobacter cloacae, streptococcus pneumoniae, enterococcus faecium, candida albicans, legionella pneumophila, candida parapsilosis, moraxella catarrhalis, neisseria meningitidis, haemophilus influenzae. |
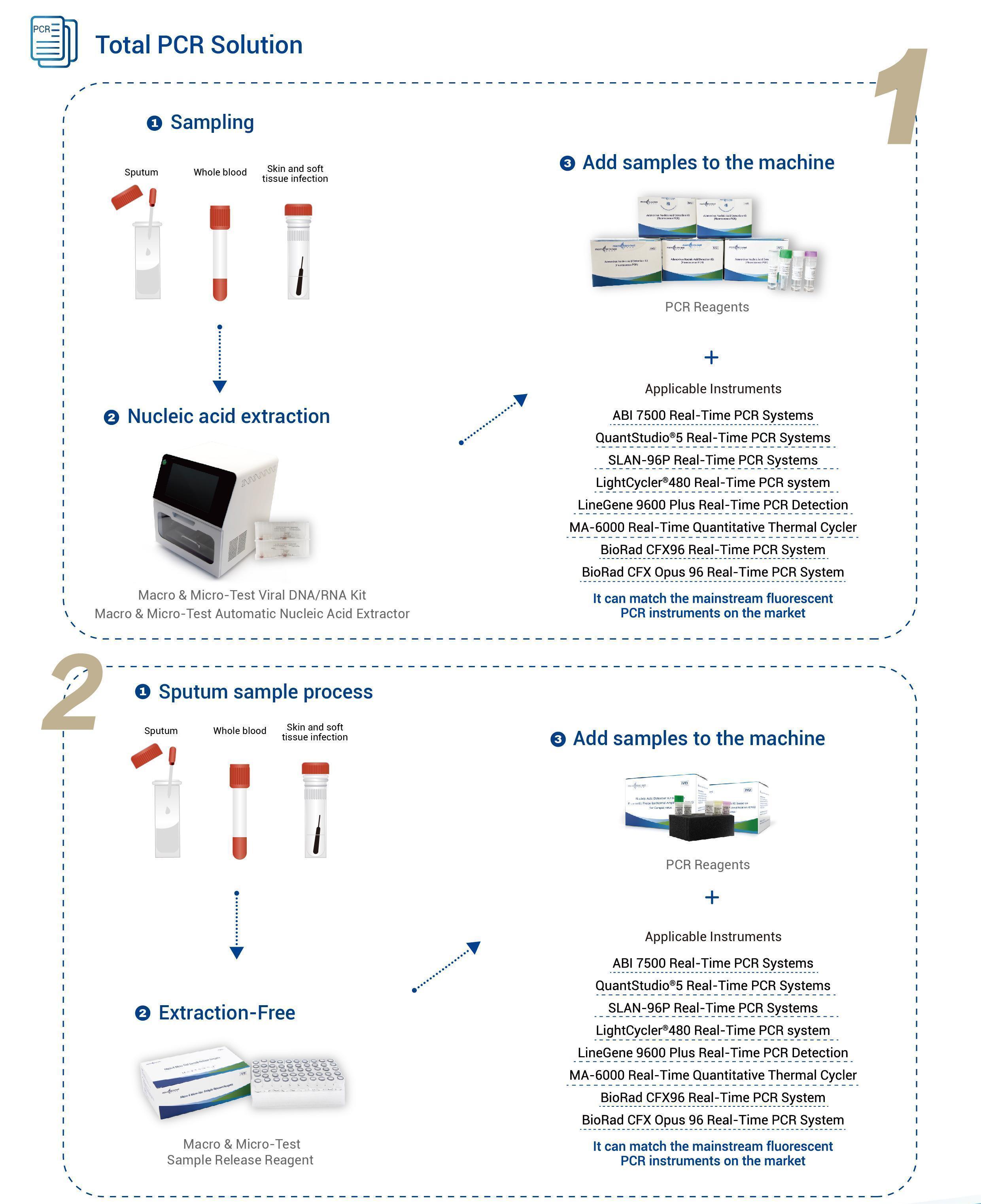
| Applicable Instruments | Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems
QuantStudio®5 Real-Time PCR Systems SLAN-96P Real-Time PCR Systems LightCycler®480 Real-Time PCR system LineGene 9600 Plus Real-Time PCR Detection System MA-6000 Real-Time Quantitative Thermal Cycler BioRad CFX96 Real-Time PCR System BioRad CFX Opus 96 Real-Time PCR System |